By Emma Murphy, Master Gardener
“If it’s not easy, you’re doing it wrong” Trudi Davidoff
For the last few years I’ve been hearing people (especially those in the native plant field) raving about winter sowing. What’s that I asked? Simple, they said – a germination method where you put seeds in an enclosed container out in your garden in winter and let Mother Nature make you more plants.
Hmm, I thought, that sounds too easy. As someone who has struggled for year with starting plants from seeds (especially annuals, vegetables, or herbs) and lost many sad looking seedlings to damping off I was intrigued.
Now I know it really is straightforward (although it requires an Ontario twist – more later) – and I am all about using a KISS principle – Keep It Simple Stupid!
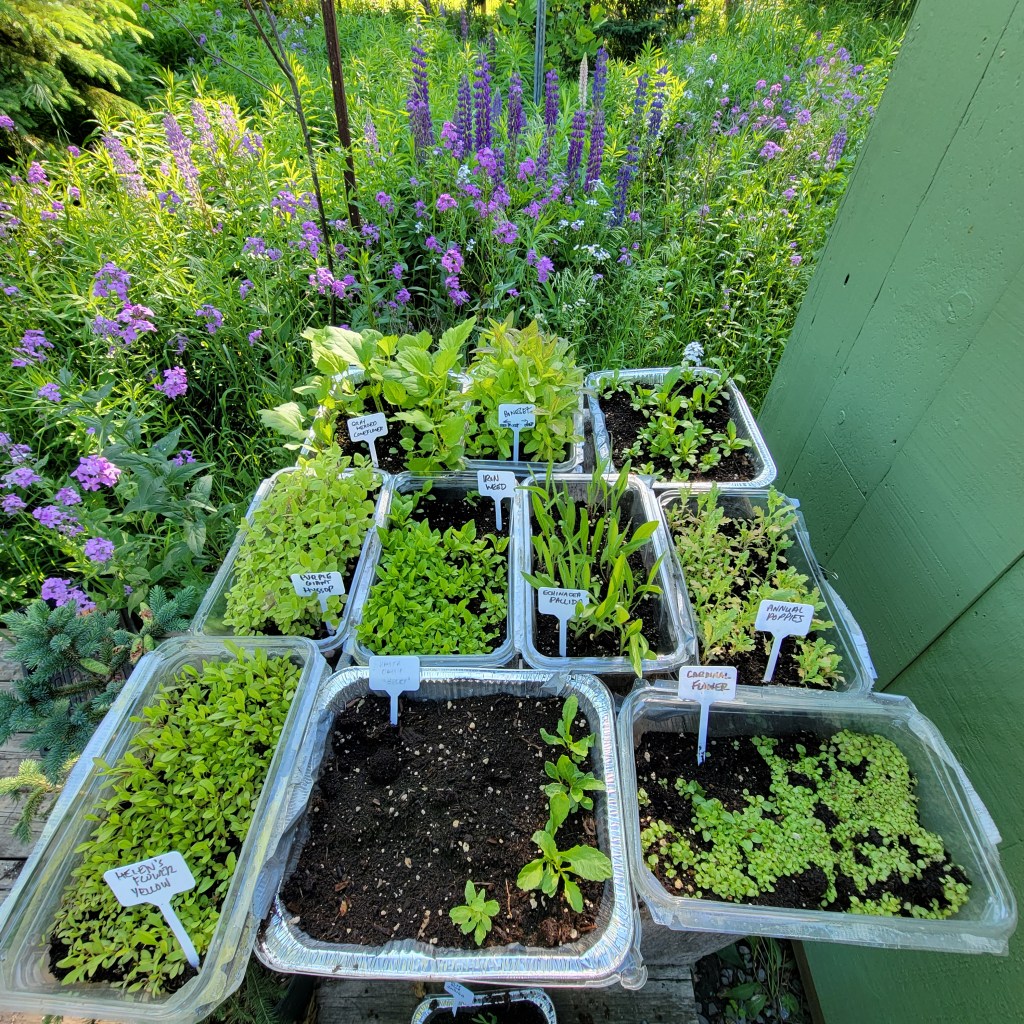

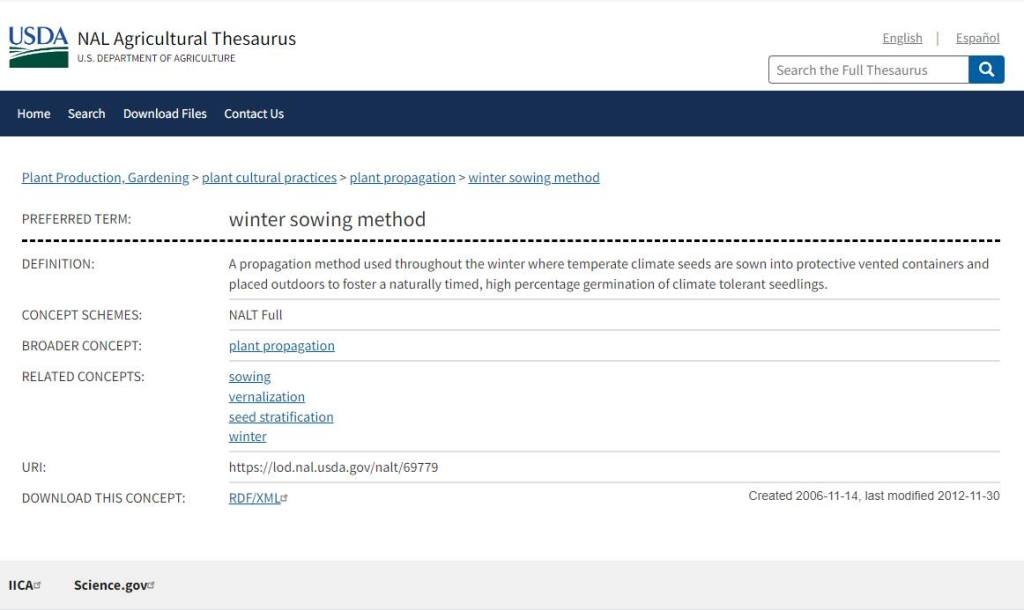
Started in 2000 by Trudi Greissle Davidoff of New York in an essay, the Winter Sowing Method is a low cost (bonus!!!), temperate climate method of producing sturdy plants for your garden. There is no need to set up lights or have a space inside your house and best of all, no hardening off process. In 2006, the U.S. Department of Agriculture recognized the viability of the technique by adding the term to the National Agricultural Library Thesaurus.
The Basics
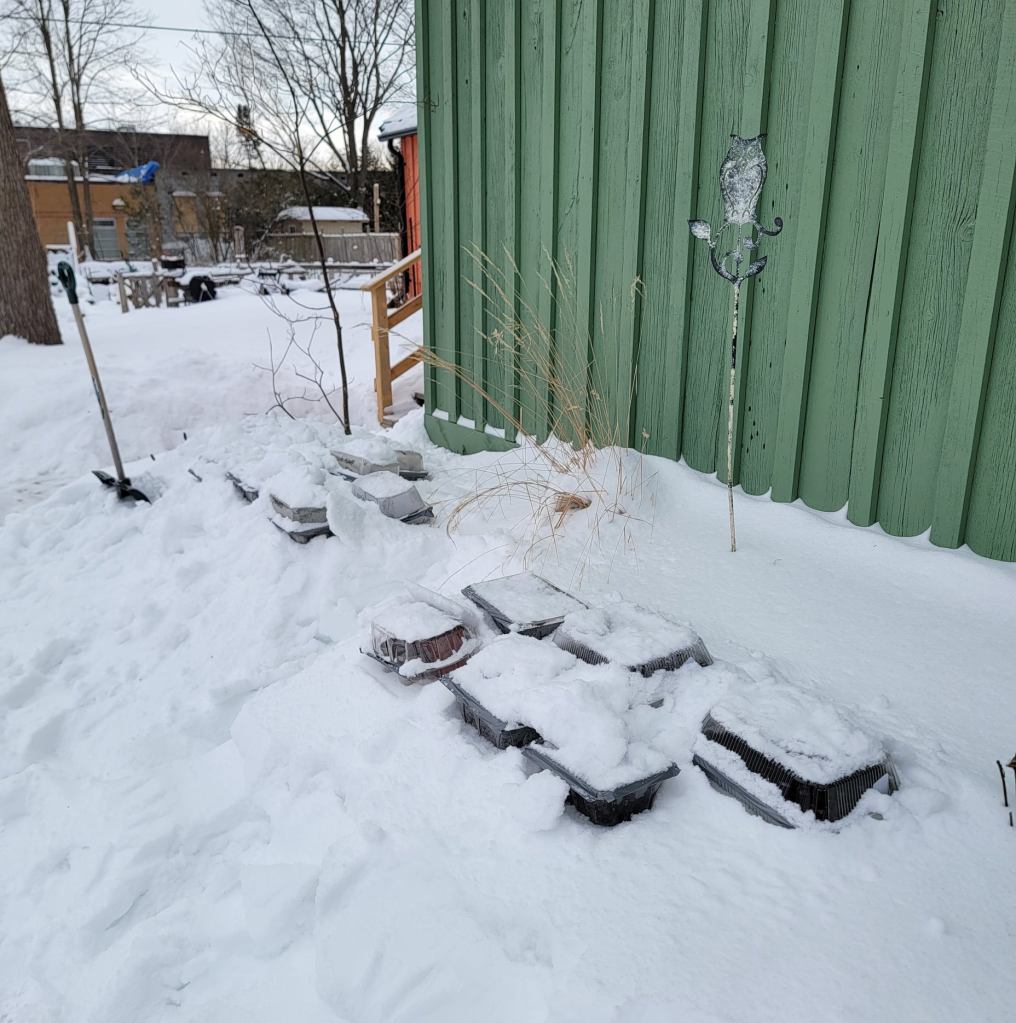
So how does it work? For winter sowing you use a recycled container (bonus!) to create a mini greenhouse that protects the seeds from animals, birds and other pests, as well as from our often variable spring weather, until they get big enough to transplant into your garden. This is one case when you actually want your seeds to be placed outdoors and exposed to the elements (including freezing temperatures, snow, and rain).
You can use any container that’s deep enough to hold sufficient potting mix and has a clear or translucent covering that is tall enough to allow the transplants to grow. It must have drainage holes in the bottom as well as ventilation holes in the top. You can use perennial or annual seeds – basically anything as long as it isn’t a tropical seed (for obvious reasons). Native seeds are particularly good because they need a period of cold stratification to germinate – why not take advantage of natural temperatures, rather than artificially refrigerating seeds that need this process?
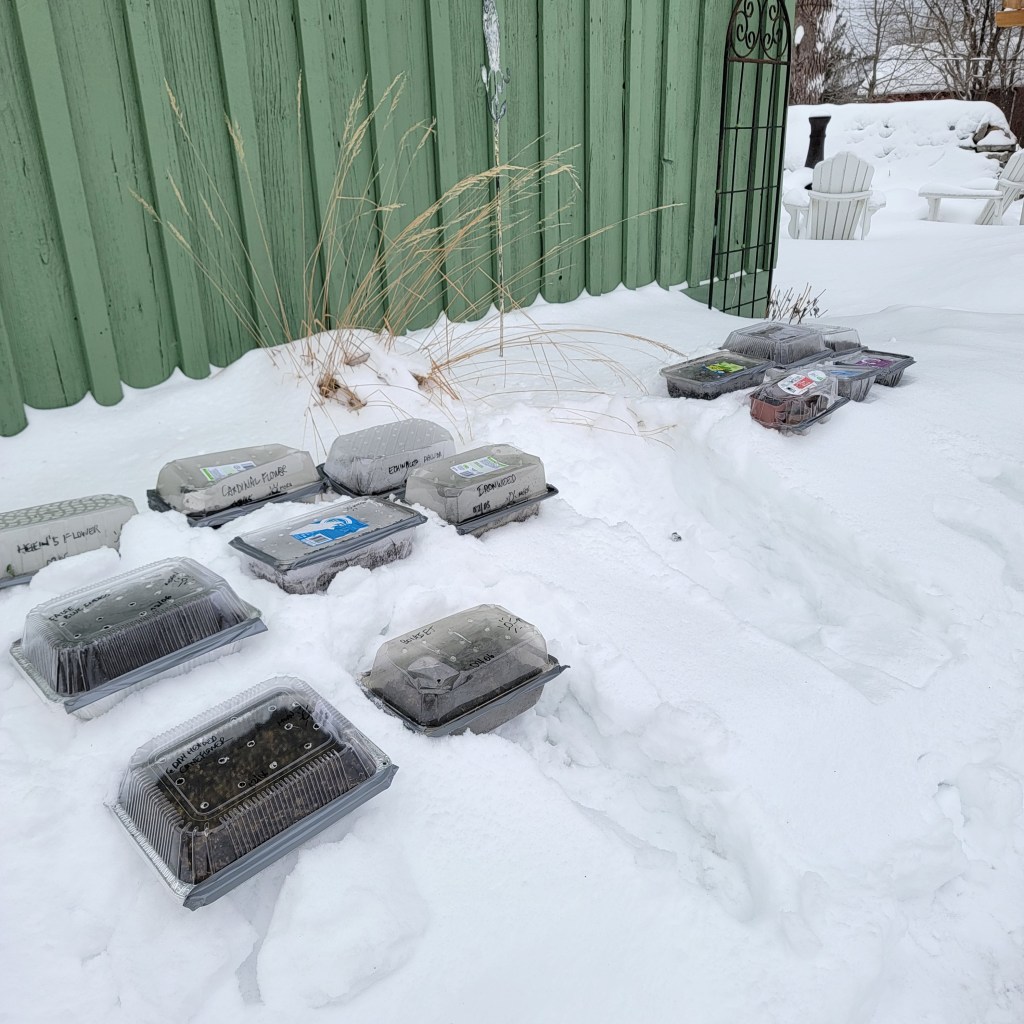

You fill the container with potting mix (at least 4-5 inches), sprinkle in your seeds, make sure the mix is moist, tape or secure the top of the container in some fashion, and put it outside. It’s good to check on the containers periodically so they don’t dry out or become waterlogged. Then you wait – it really is that simple.
Ok, I know there are questions – When do I start where I live? When do I plant x seeds? What soil do I use? Let me try and answer some of the basic ones and point you to other resources as well.
Trudi’s original website is no longer active but there is a very active Facebook page that follows her method – Winter Sowers – which I highly recommend for all the basic information and lively discussions amongst members. Trudi is an admin on the page.
Timing for Winter Sowing?
You can start winter sowing anytime after the Winter Solstice (December 21st). Perennials are generally done first, as they often require (or benefit from) cold stratification, then hardy annuals, then tender annuals. But the bottom line is that the seeds will germinate when the conditions are right for each kind of seed. That is the beauty of winter sowing! Many people winter sow their perennials in January but then wait until March to start their annuals. It really doesn’t matter – do what works for you!
They are ready to plant whenever the outside temperature has sufficiently warmed and they are the right size (2 to 3 inches or more importantly at least two sets of real leaves).
What Soil to use?
It’s recommended to use a sterile potting soil mix; avoid soil bags that say they are ‘weed free’ because they can contain chemicals mixed into soil to prevent any weed seeds in that bag from germinating. So they will also prevent the germination of seeds you sow in that same soil! If you live in an extremely dry environment, you might want to use soil that has moisture retentive crystals – otherwise this is not necessary (and can even be a problem in wet winter regions like the U.S. Pacific Northwest). Using fertilized soil for a sowing medium is a personal preference.
What Containers? The Ontario Twist
Most winter sowers tend to use milk jugs for their seeds, but these are not readily available in Ontario – we still love our milk bags! But the reality is that you can use any container for winter sowing as long as it can hold at least 3 inches (7.6 cm) of potting soil. I have seen various other things used – juice bottles, clear pop bottles, blue and green bottles, aluminum pans, salad boxes, plastic containers, pretzel barrels, cheese curl containers, ice cream buckets, nut containers, and vinegar jugs. They must be translucent (some light passes through) or transparent (all light passes through). Opaque materials will not work. Personally I have used the large fresh spinach containers or aluminum roasting pans with clear lids.
You do need some sort of cover on your container, as it helps keep heavy rains under control (so they drip slowly into your containers), it keeps more moisture in so that you have a higher germination rate of your seeds, and it keeps weed seeds out of your containers.
How do I Label?
Labelling is really important unless you’re a genius at identifying new sprouts! I recommend putting in two labels – one on the underside of your tray and one on a popsicle stick in the container. Trudi recommends using duct tape and an industrial sharpie. Tip – place your labels before you fill the tray with soil and put them so they don’t impede the water drainage holes. There is lots of discussion on the best pens to use for labelling – everything from paint pens to garden markers, livestock markers, and china/grease markers.
This will be my second year winter sowing just north of Peterborough – I learned a lot in my first year, most importantly to transplant my seedlings before they get too big and dry out. I wrote a blog earlier this year about some of the cool native plants that I winter sowed last winter.
I hope this blog encourages you to consider winter sowing for your garden, particularly for native species to your area – seeds are so much cheaper than plants and then once they go to seed you are all set to grow even more plants, either for yourself or to share with friends!

Want More Information?
Some videos (and posts) you may want to check out – there are lots of winter sowing videos out there (sometimes with conflicting information) but these are two that are recommended by the online group
Dolly Foster – Hort4U Winter Sowing Presentation
All The Dirt on Winter Sowing
Planting Native Seeds (Facebook link)
WinterSowing 101 – Jug Prep (if you have milk jugs) (Facebook link)
Frequently Asked Questions (Facebook link)
































